Schizophrenia Mental Disorder
What is Schizophrenia?
Studies have shown that people with a family history of schizophrenia are more likely to develop the disorder. Additionally, certain environmental factors, such as stress and exposure to certain toxins, may also increase the risk of developing schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia also affects a person's emotions
and motivation. People with schizophrenia may appear to be emotionally
flat or "blunted," meaning they don't show emotions in the way that
most people do. They may also lack motivation and have difficulty with
activities of daily living.
Symptoms of Schizophrenia:
Delusions, hallucinations, disorganized
thinking & speech are other symptoms of schizophrenia. This can include
talking in a rambling or nonsensical way or having trouble connecting thoughts
or ideas.
People with schizophrenia may also have trouble
focusing or completing tasks. It also affects a person's emotions and motivation. People
with schizophrenia may appear to be emotionally flat or "blunted,"
meaning they don't show emotions in the way that most people do. They may also
lack motivation and have difficulty with activities of daily living.
The exact cause of schizophrenia is not yet
fully understood, but research suggests that a combination of genetic,
environmental, and psychological factors play a role.
There is some evidence to suggest that certain herbs and plants may be useful in treating symptoms of schizophrenia. Some examples include:
Ashwagandha:
This
herb, also known as Indian ginseng, has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for
centuries to treat a variety of ailments, including anxiety and stress. Studies
have found that ashwagandha may help to improve symptoms of schizophrenia, such
as positive and negative symptoms, as well as cognitive function.
Holy basil:
It is also known as Tulsi, holy basil is an herb that has been traditionally used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat a variety of mental health conditions, including anxiety and depression. Some studies have suggested that holy basil may help to improve symptoms of schizophrenia.
This is a compound found in the cannabis plant.
Studies have found that CBD may help to improve symptoms of schizophrenia, such
as positive symptoms, as well as cognitive function.
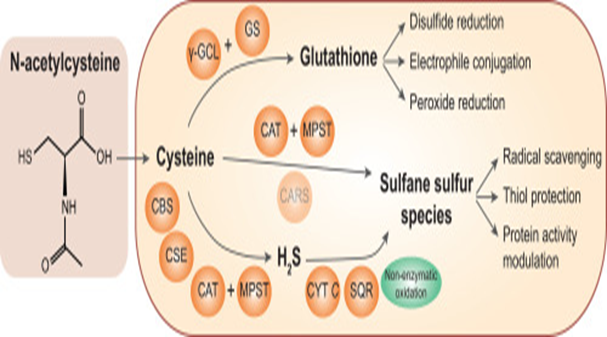
N-acetylcysteine (NAC):
NAC is an amino acid that has been found to
improve symptoms of schizophrenia, including negative symptoms and
cognitive function.
It's important to note that these herbs
and plants should not be used in place of medications prescribed by a
healthcare professional, but rather as a complementary therapy under the
guidance of a healthcare professional.
What are 5 causes of Schizophrenia:
Genetics:
Studies have shown that schizophrenia runs in
families, and certain genetic variations may increase the risk of developing
the disorder.
Brain chemistry:
Abnormalities in the levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and glutamate, have been associated with schizophrenia.
Medications, specifically antipsychotics, are
the primary treatment for schizophrenia. Antipsychotics work by altering
the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, specifically dopamine,
which can help reduce symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and
disordered thinking. Some common antipsychotic medications include:
Brain structure:
Researchers have found differences in the size
and structure of certain brain regions in people with schizophrenia, such as
the hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex.
Environmental factors:
Exposure to certain environmental factors, such
as viral infections, malnutrition, and stress, during critical periods of brain
development, may increase the risk of developing schizophrenia.
Prenatal factors:
Exposure to certain prenatal factors, such as
malnutrition, viral infections, and stress, has been linked to an increased
risk of schizophrenia in the offspring.
There are several tests and assessment tools that can be used to diagnose schizophrenia.
1. The Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 (SCID-5) h:
It is a diagnostic interview used to determine whether an individual meets the criteria for a specific mental disorder, such as schizophrenia.
2. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS):
It is a rating scale that assesses the positive symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusions), negative symptoms (e.g., lack of motivation, flat affect), and general psychopathology of schizophrenia.
3. The Schizophrenia Positivity Scale (SOPS):
It is a rating scale that assesses the presence and severity of positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
4. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS):
It is a rating scale that assesses the severity
of psychiatric symptoms, including those commonly seen in schizophrenia, such
as hallucinations and delusions.
It is important to note that these tests and assessments are typically administered and interpreted by a trained mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist.
A diagnosis of schizophrenia can only be made after a comprehensive evaluation that includes a thorough medical, psychological, and social history, as well as a physical examination.
- Chlorpromazine
- Fluphenazine
- Haloperidol
- Risperidone
- Olanzapine
- Quetiapine
- Aripiprazole
It is important to consult with a doctor before
taking any medication, including herbal supplements, as they can interact with
other medications you may be taking and have potential side effects. It is
always best to speak with a healthcare professional before starting any new
treatment.
Which Chemicals are responsible for Schizophrenia Problems?
The dopamine and glutamate hypotheses
propose that imbalances in the levels of these neurotransmitters in the
brain may contribute to the development of the disorder. Other chemicals that
have been linked to schizophrenia include GABA, serotonin, and neurotrophic
factors.
Dopamine Hypothesis:
One of the leading theories of the cause of schizophrenia is the dopamine hypothesis, which suggests that an imbalance in the levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain is responsible for the disorder. Dopamine is a chemical messenger that plays a key role in regulating mood, motivation, and movement. Research has shown that people with schizophrenia have abnormal levels of dopamine in certain areas of the brain, specifically the mesolimbic pathway, which is involved in the regulation of reward and motivation.
Glutamate Hypothesis:
Another theory is the glutamate hypothesis, which suggests that an imbalance in the levels of the neurotransmitter glutamate in the brain is responsible for the disorder. Glutamate is a chemical messenger that plays a key role in regulating brain function, including memory, learning, and perception. Research has shown that people with schizophrenia have abnormal levels of glutamate in certain areas of the brain, specifically the prefrontal cortex, which is involved in the regulation of cognitive function.
Other chemicals that
have been linked to the development of schizophrenia include:
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA):
It is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps to regulate the activity of the brain.
Serotonin:
It is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating
mood, appetite, and sleep.
Neurotrophic factors are chemicals that help to
promote the growth and survival of neurons in the brain.
It's important to note that this is a complex
disorder, and many other factors such as environmental or epigenetic also play
a role in its development. Furthermore, research is ongoing to better
understand how these chemical imbalances interact with other factors to cause
schizophrenia.








Comments
Post a Comment